When I write on my iPad mini, I often need to look up and reference price of apps that I already own. That’s a surprisingly hard thing to do on an iOS device, so I decided to remove the annoyance caused by this problem with an Editorial workflow. I call it “Get App Price”.
If you own an app, searching for it in the iOS 7 App Store won’t show you the price information alongside the app’s icon and description – you’ll only get an Open or Install button. Unlike the Mac App Store, there is no separate pricing field in the app information at the bottom of the screen, which usually forces me to go to a developer’s website to find out what the price of an app is.1 There wouldn’t be any problem if Apple allowed Safari to open iTunes web previews without redirecting them straight to the App Store, which is what they do on OS X. I have tried to force Safari to open web previews, and I even downloaded browsers that can set a modified user agent string to trick iOS into thinking they’re desktop web browsers worthy of a web preview – eventually, the App Store app always opened, displaying no price.
I set out to create a simple workflow to fetch an app’s title and price directly from iTunes with no clipboard import or other middleman. I later found out that you can tap on the “Related” tab in the App Store or gift an app to view its price, but I had already created a workflow that’s faster than opening the App Store and tapping a bunch of buttons just to get a price. I’m a free man, and I deserve my own App Store lookup solution.2
The workflow is a simple way of querying the iTunes Search API and parsing a JSON response with Python, displaying results in a popover. The fact that this stuff is possible on an iPad never ceases to amaze me.
You can find documentation for the iTunes Search API here. Essentially, you need to construct a URL that contains parameters for media type, entity (iPhone apps, iPad apps, Mac apps), store (US, UK, etc), and input (your search term). Given this URL, a response is sent back containing results that can be parsed with JSON and displayed by extracting specific information from them and re-arranging them as we like in a visual list.
To make things more fun and integrated, I added support for affiliate links with tokens and campaign tracking codes. In the workflow, you will need to fill in this information with your affiliate data, otherwise leave them empty and you’ll still find and generate valid iTunes URLs. You can find out more about the iTunes affiliate program here.
Last, Markdown. The workflow can be used to just quickly look up a price, but if you go ahead and tap a result in a list, a Markdown link will be inserted in the text editor. But enough with the talking.
The workflow starts by asking you to add your affiliate token and campaign tracking code. These need to be in the &at=TOKEN and &ct=CAMPAIGN format, otherwise they won’t create a valid affiliate link. You can leave both empty if you don’t care, or leave the campaign empty if you don’t need it and just use an affiliate token. Both values are handled as variables in the workflow. If you need a refresher on the new affiliate links, Underscore’s article is a great place to start.
The workflow then asks you what type of app you’re looking for; this list will output a value that will be used for the entity parameter of the search API URL. Alas, results that aren’t specific to a single platform (such as iPhone + iPad apps) haven’t been that good in my experience. You need to pick one.
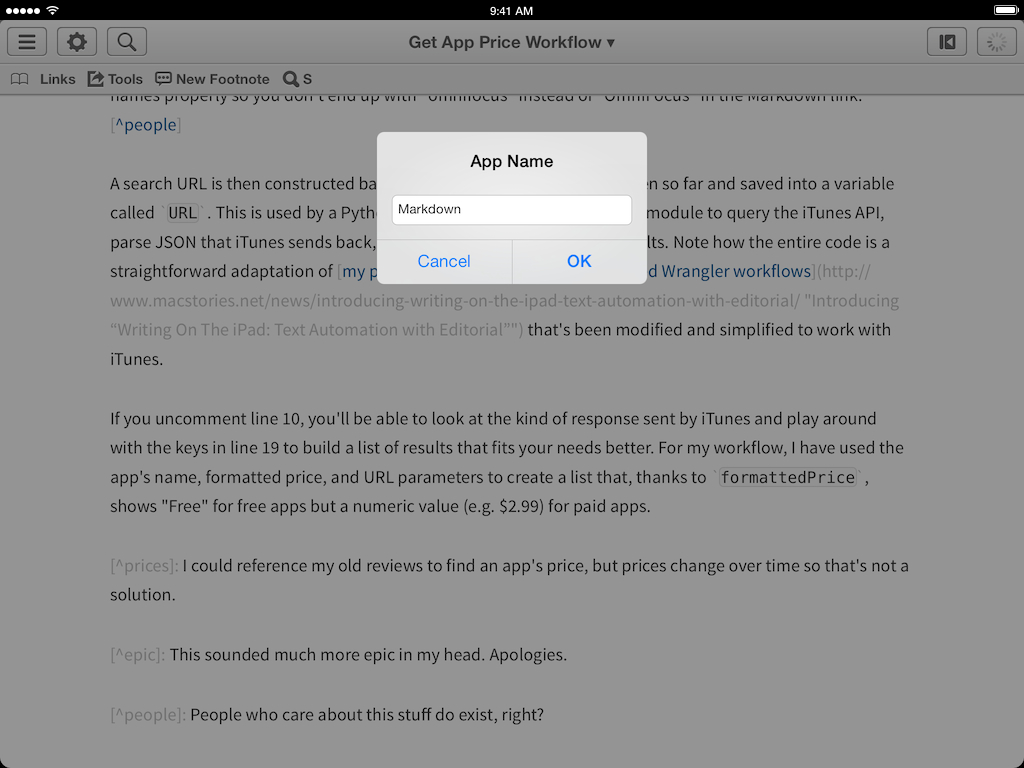
After the app type, the workflow will ask for an app’s name and save what you enter in a variable. The name you enter has two purposes: it’s used as a search term and it becomes the title of the Markdown link that can be optionally inserted in the editor. If you want to be extra picky, my suggestion would be to type app names properly so you don’t end up with “omnifocus” instead of “OmniFocus” in the Markdown link.3
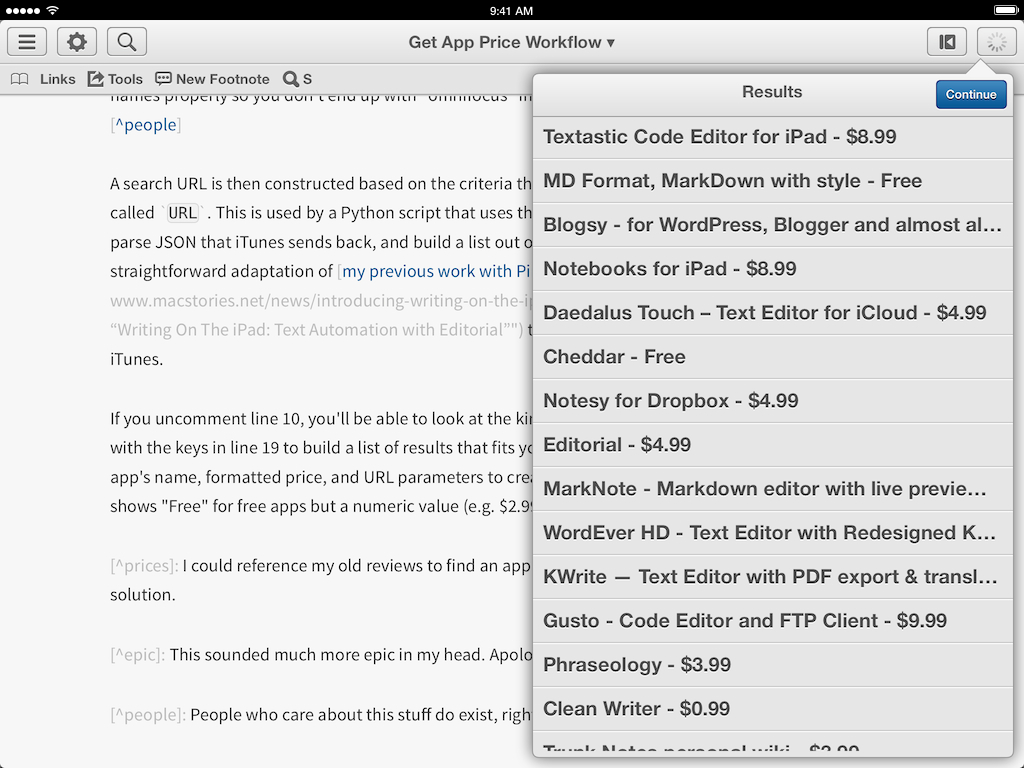
A search URL is then constructed based on the criteria that you’ve chosen so far and saved into a variable called URL. This is used by a Python script that uses the requests module to query the iTunes API, parse JSON that iTunes sends back, and build a list out of available results. Note how the entire code is a straightforward adaptation of my previous work with Pinboard and Feed Wrangler workflows that’s been modified and simplified to work with iTunes.
If you uncomment line 10, you’ll be able to look at the kind of response sent by iTunes and play around with the keys in line 19 to build a list of results that fits your needs better. For my workflow, I have used the app’s name, formatted price, and URL parameters to create a list that, thanks to formattedPrice, shows “Free” for free apps but a numeric value (e.g. $2.99) for paid apps. At the end of the workflow, the final (affiliate or not) iTunes link is assembled, inserted in the editor, and copied to the clipboard is you tapped a result from the list of results.
Automated workflows don’t change lives but they can help you save time that you’d spend yelling at a computer. This is one of them. It’s saving me minutes I can spend doing other things that I enjoy such as hugging my girlfriend or FaceTiming my parents. You can download it here.