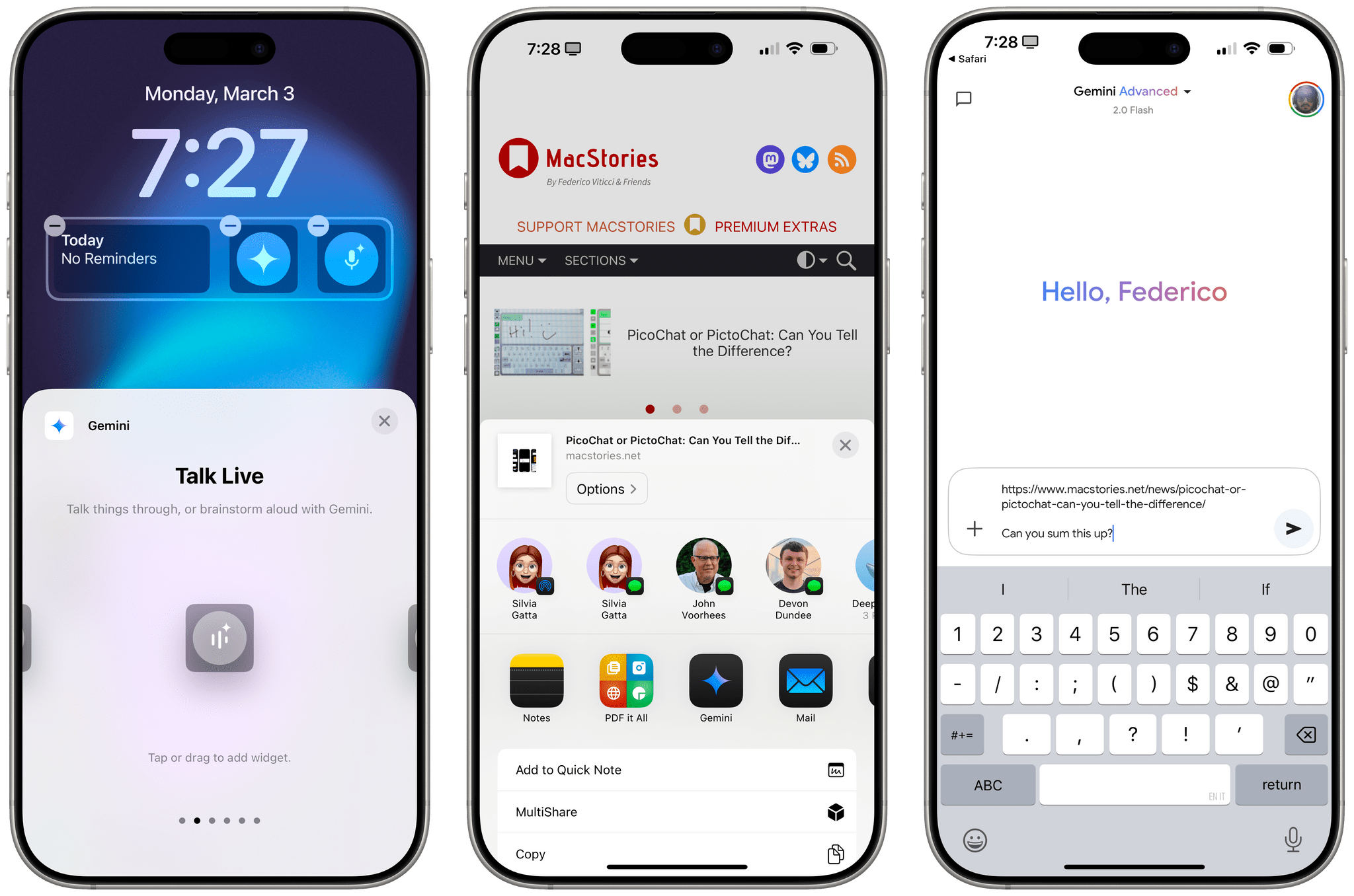
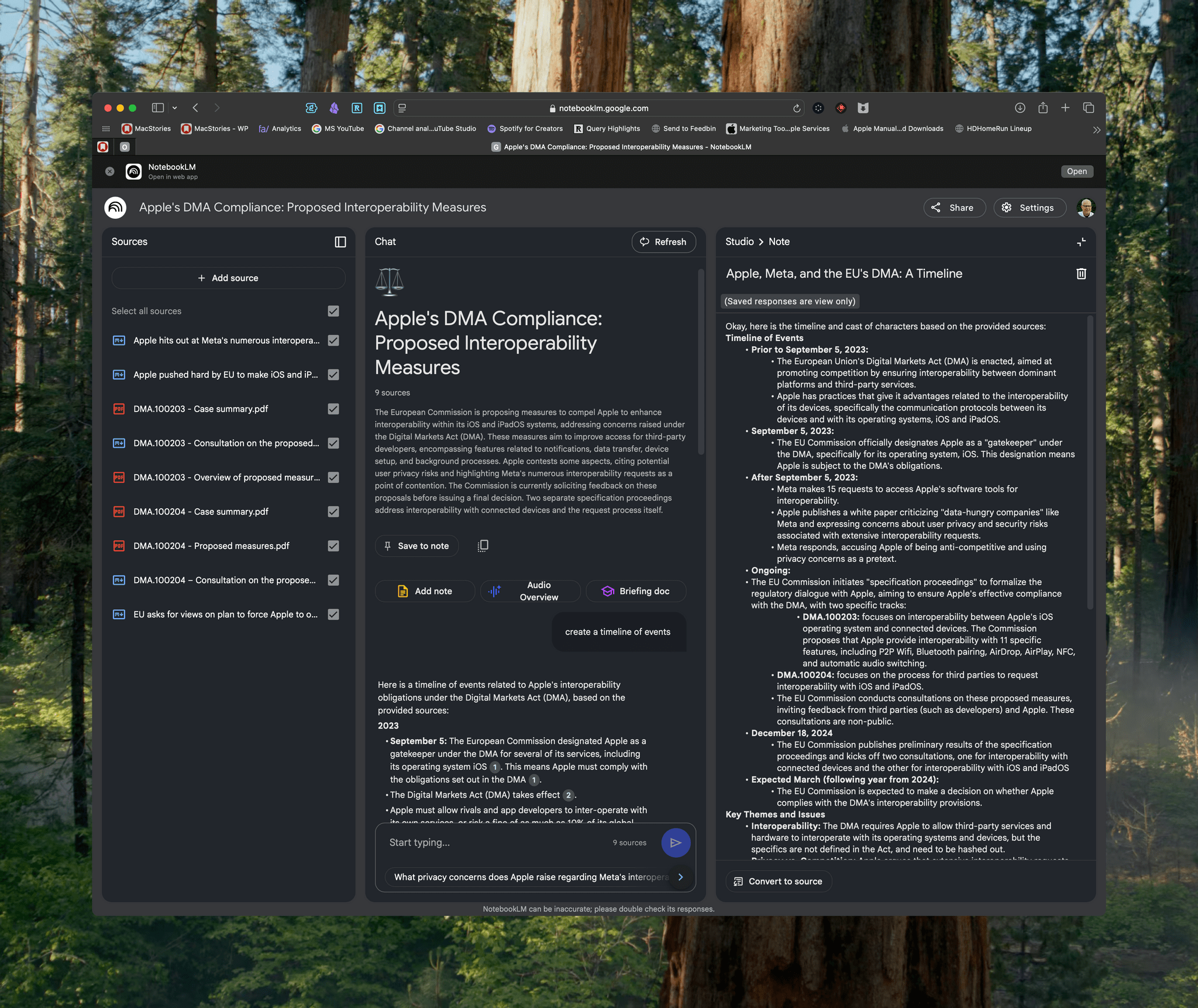
When I last wrote about Gemini for iOS, I noted the app’s lackluster integration with several system features. But since – unlike others in the AI space – the team at Google is actually shipping new stuff on a weekly basis, I’m not too surprised to see that the latest version of Gemini for iOS has brought extensive support for widgets.
Specifically, Gemini for iOS now offers a collection of Lock Screen widgets that also appear as controls in iOS 18’s Control Center, and there are barebones Shortcuts actions to go along with them. In both the Lock Screen’s widget gallery and Control Center, you’ll find Gemini widgets to:
- type a prompt,
- Talk Live,
- open the microphone (for dictation),
- open the camera,
- share an image (with a Photos picker), and
- share a document (with a Files picker).
It’s nice to see these integrations with Photos and Files; notably, Gemini now also has a share extension that lets you add the same media types – plus URLs from webpages – to a prompt from anywhere on iOS.
The Shortcuts integration is a little less exciting since Google implemented old-school actions that do not support customizable parameters. Instead, Gemini only offers actions to open the app in three modes: type, dictate, or Talk Live. That’s disappointing, and I would have preferred to see the ability to pass text or images from Shortcuts directly to Gemini.
While today’s updates are welcome, Google still has plenty of work left to do on Apple’s platforms. For starters, they don’t have an iPad version of the Gemini app. There are no Home Screen widgets yet. And the Shortcuts integration, as we’ve seen, could go much deeper. Still, the inclusion of controls, basic Shortcuts actions, and a share extension goes a long way toward making Gemini easier to access on iOS – that is, until the entire assistant is integrated as an extension for Apple Intelligence.