Today, Apple revealed the latest updates to Final Cut Pro for the Mac and iPad, with both offering a variety of new features and simplified workflows.
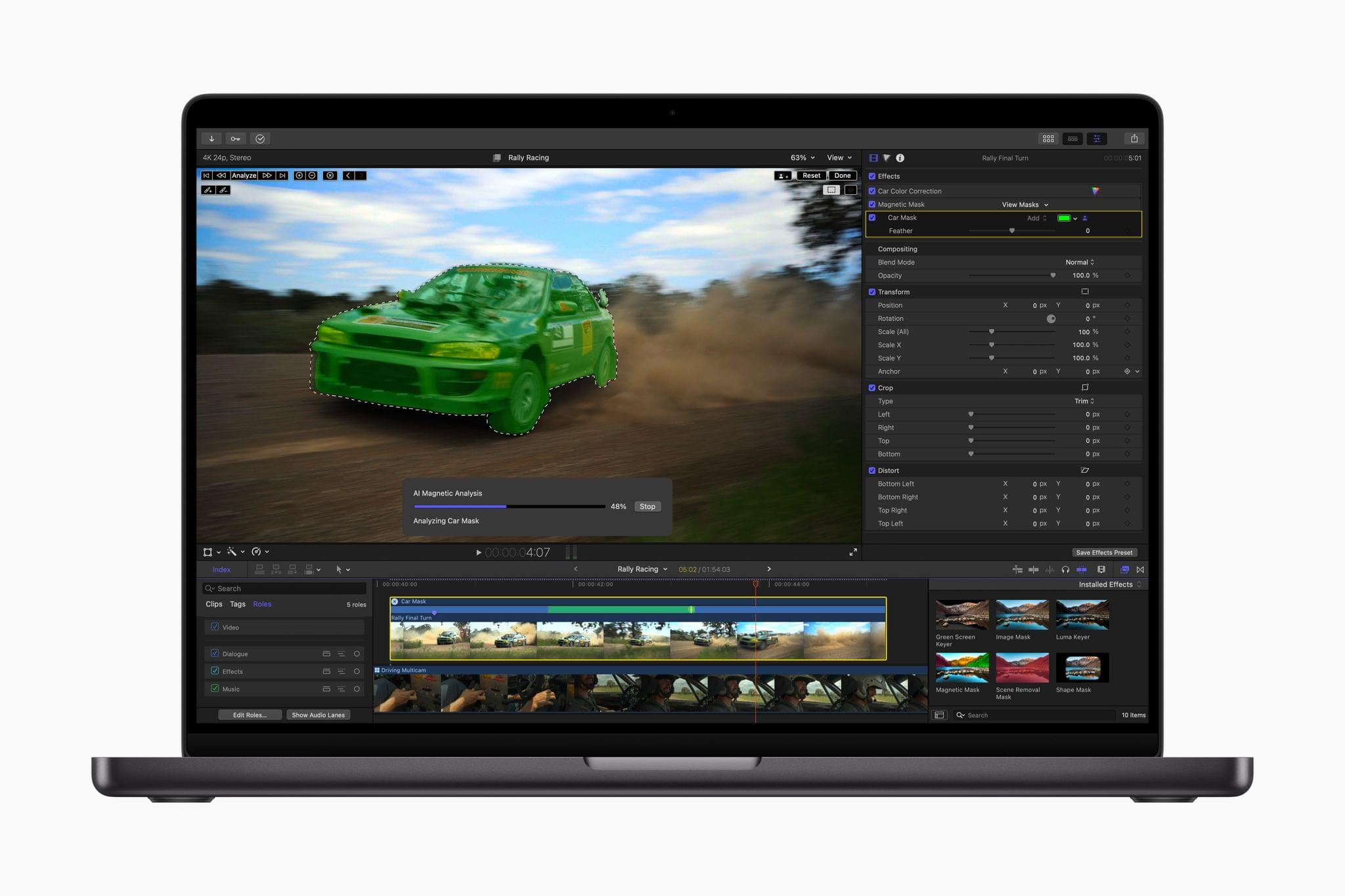
Final Cut Pro 11 for the Mac has added magnetic masks, extending the “magnetic” metaphor used for clips placed on your timeline. Apple says the new feature will allow you to quickly mask people and objects in a shot to color grade them or add effects separately from the rest of a scene.
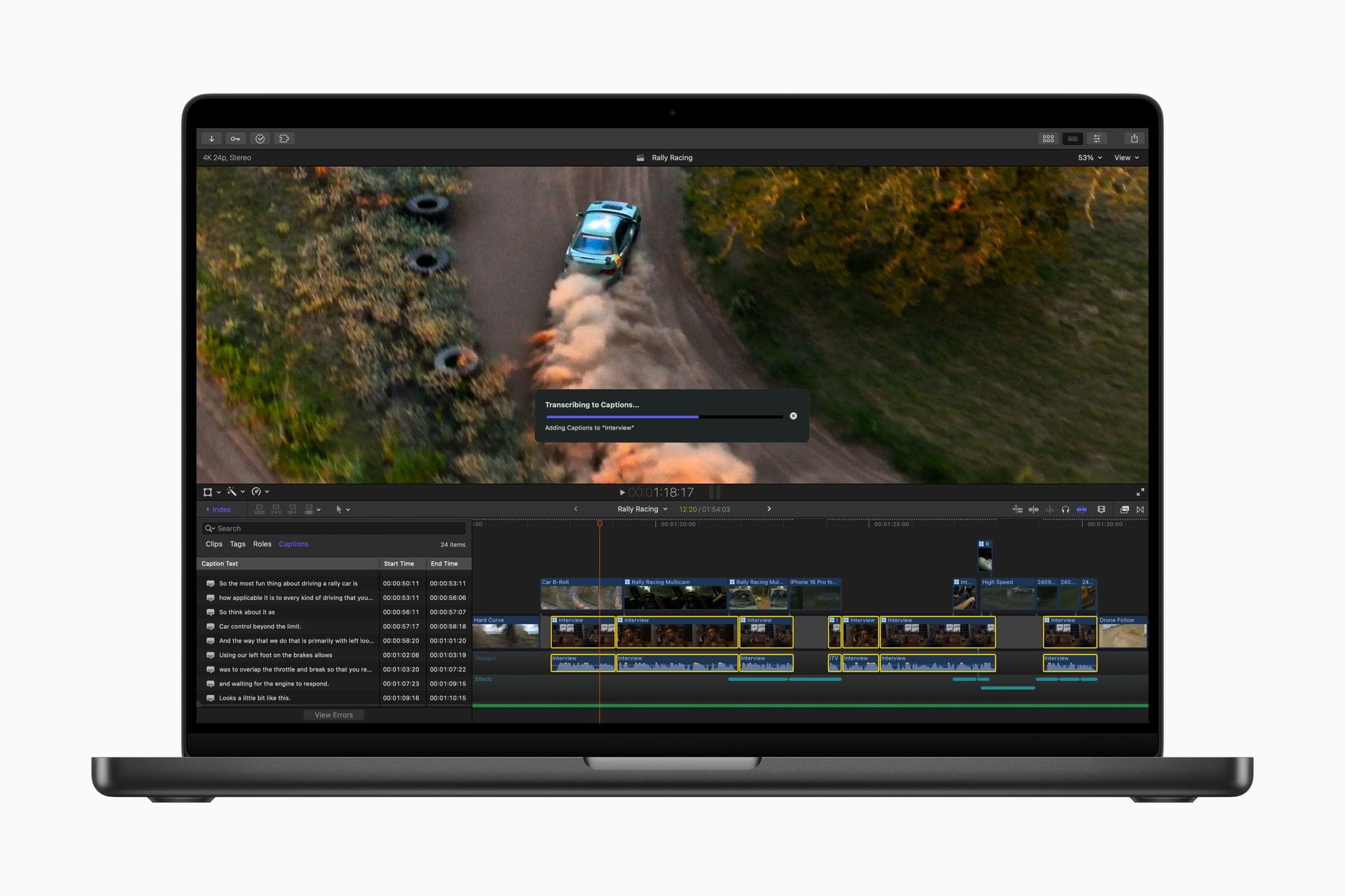
The app can automatically generate closed captions now, too. The feature, which was briefly shown off in a video published alongside the announcement of the new Mac mini, uses artificial intelligence to convert dialogue into text.
Final Cut Pro 11 is also now capable of editing spatial video for the Apple Vision Pro. In its press release, Apple says:
Final Cut Pro 11 now supports spatial video editing, allowing editors to import their footage and add effects, make color corrections, and enhance their projects with titles. The depth position of titles and captured footage can also be adjusted during the editing process. Spatial video clips can be captured directly with Vision Pro, or on iPhone 15 Pro, iPhone 16, iPhone 16 Pro, and Canon’s new RF-S7.8mm F4 STM DUAL lens paired with Canon R7.
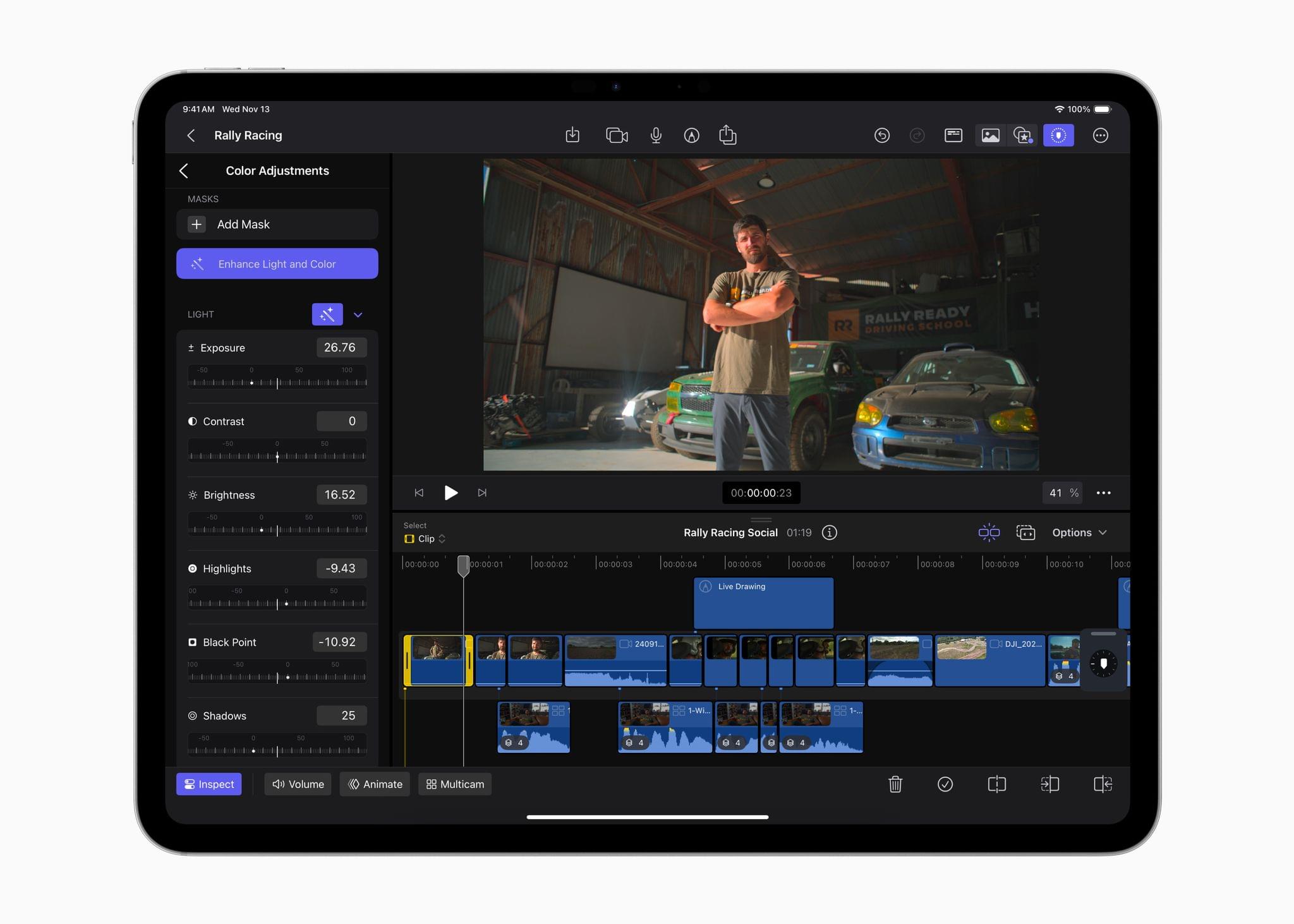
Final Cut Pro for the iPad has been updated to version 2.1 with several new features. I’ve been using Final Cut Pro more regularly since we started the MacStories YouTube channel, and one of the limitations I noticed immediately is that the color correction tools in the iPad version weren’t nearly as good as on the Mac. The iPad’s color tools still aren’t as sophisticated as what’s available on the Mac, but this update does add new color grading presets as well as a new Enhance Light and Color feature that intelligently applies color, contrast, brightness, and color balance to a video and works with SDR, HDR, RAW, and Log-encoded media.
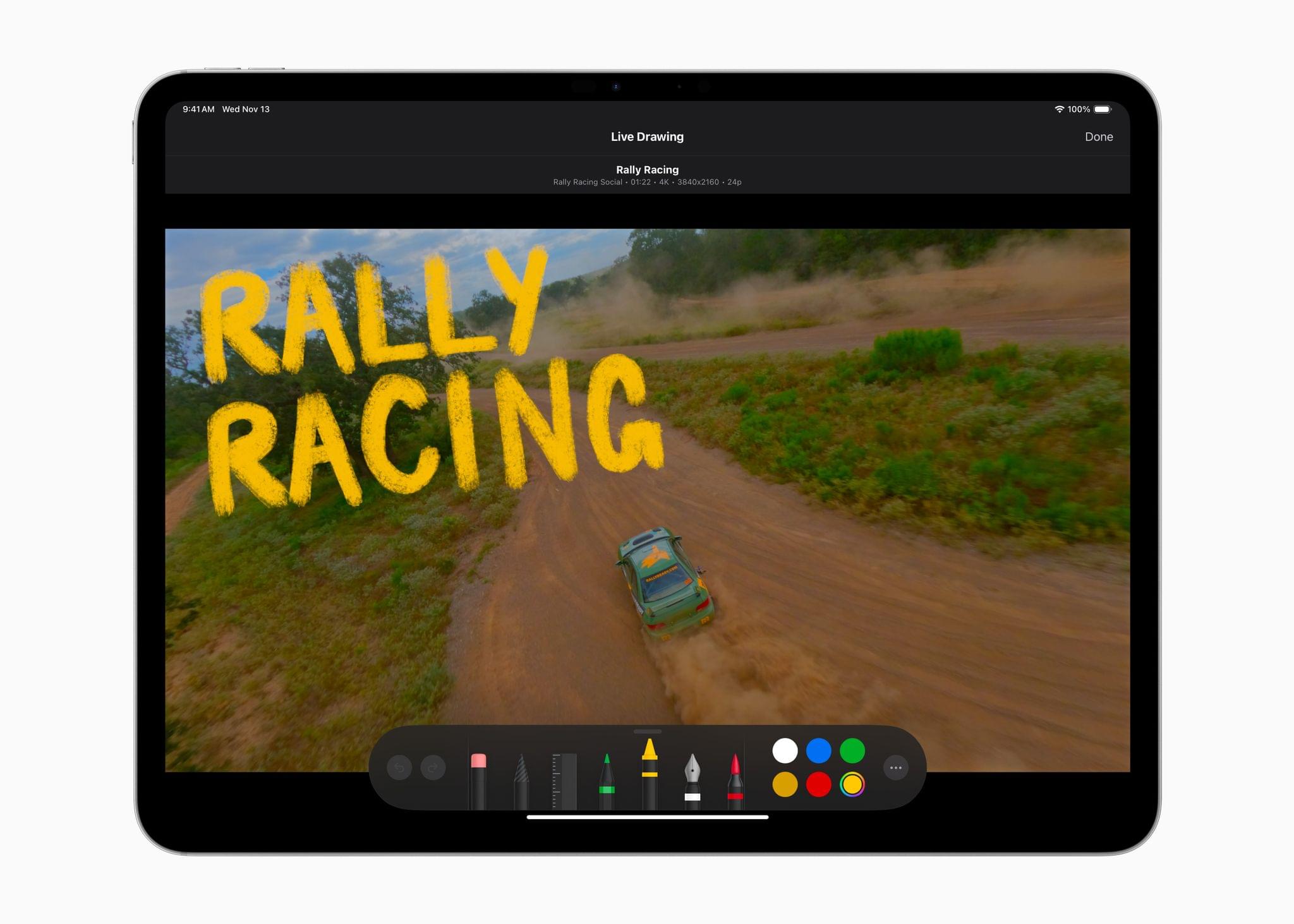
Live Drawing on a video has been expanded with new brushes, too. There are new watercolor, crayon, fountain pen, and monoline pen brushes, letting users create a greater variety of looks for their videos. Other new effects include a picture-in-picture effect, callouts, and a set of built-in soundtracks. I’m eager to try picture-in-picture, which should be a good way to create tutorials and other types of videos and callouts; it’s an effect available from multiple third-party effects vendors on the Mac, but new to the iPad.
The iPad version of Final Cut Pro is also adding a host of other new features, including:
- the ability to expand clips in the timeline vertically with a pinch gesture,
- dynamic adjustments to the size of the picture-in-picture window,
- support for editing high-frame-rate video, and
- Apple Pencil Pro haptic feedback for timeline scrubbing and dropping effects onto the timeline.
Read more