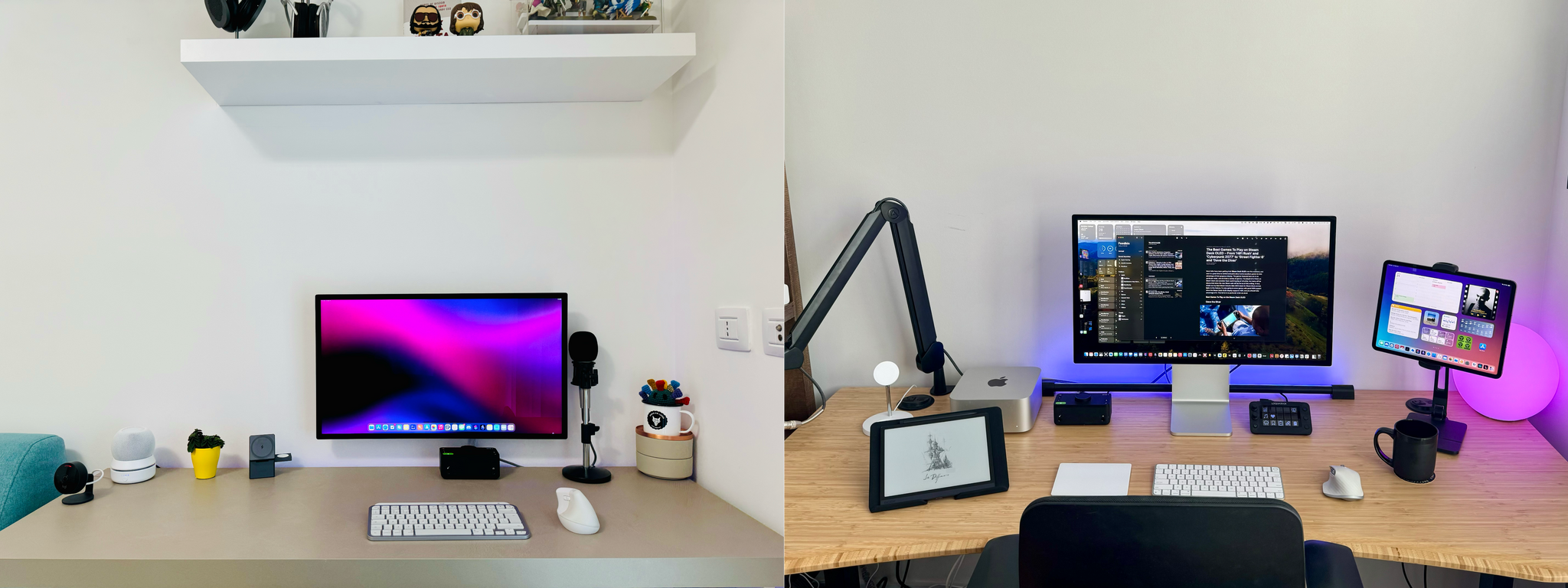
When Federico and I published our setups last November, I was happy with mine, but there was still something that bothered me. Every day, I wound up with too much stuff strewn across my desk. At the same time, some of the things I use most days felt annoyingly out of reach. These weren’t monumental annoyances, but they were daily distractions that led me to leave things on my desk for long stretches of time where they were in the way. So, I started thinking about ways to improve my setup again.
What I realized is that I had nowhere to put any of the little things I use each day, so they’d end up all over my desk, which then snowballed into a bigger mess. The solution was to bring those little things closer but create places for them that are out of the way. At the same time, I made a greater effort to tuck cables and wires out of the way where I can’t see them, which has also helped cut down on clutter.
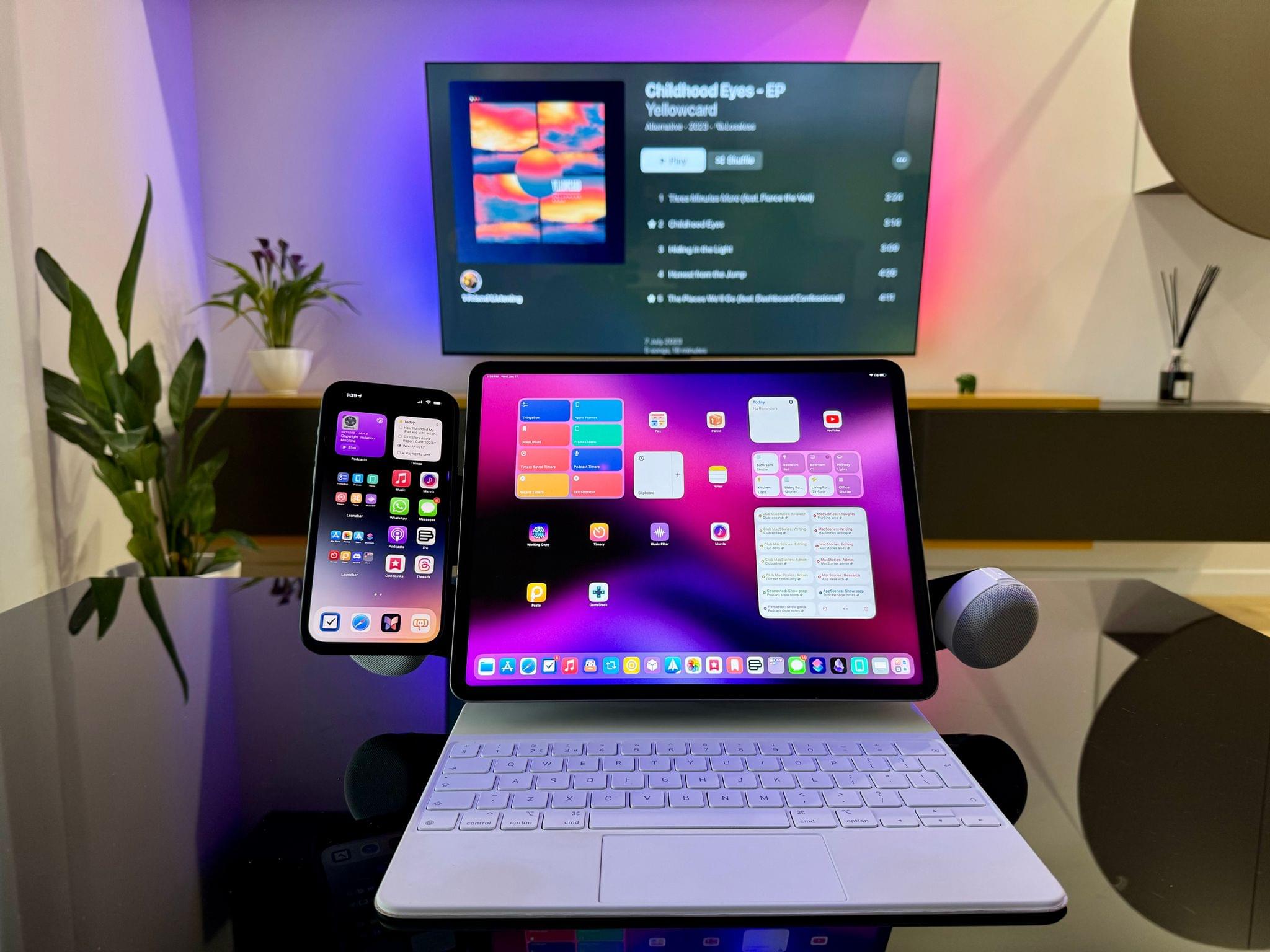
The centerpiece of this revised setup is a Balolo Setup Cockpit. There are a lot of companies that make desk shelves, but they never appealed to me because I’ve always been able to adjust my Studio Display to a comfortable height without one. I could tuck things under the shelf, but I needed more than that.
What I like about the Balolo shelf is that it has a system of attachment points on the underside of the shelf for adding accessories that have allowed me to get more off my desk and out of the way. It’s turned out to be the perfect floating, modular extension of my old setup that makes a long list of small adjustments that add up to a big difference overall.