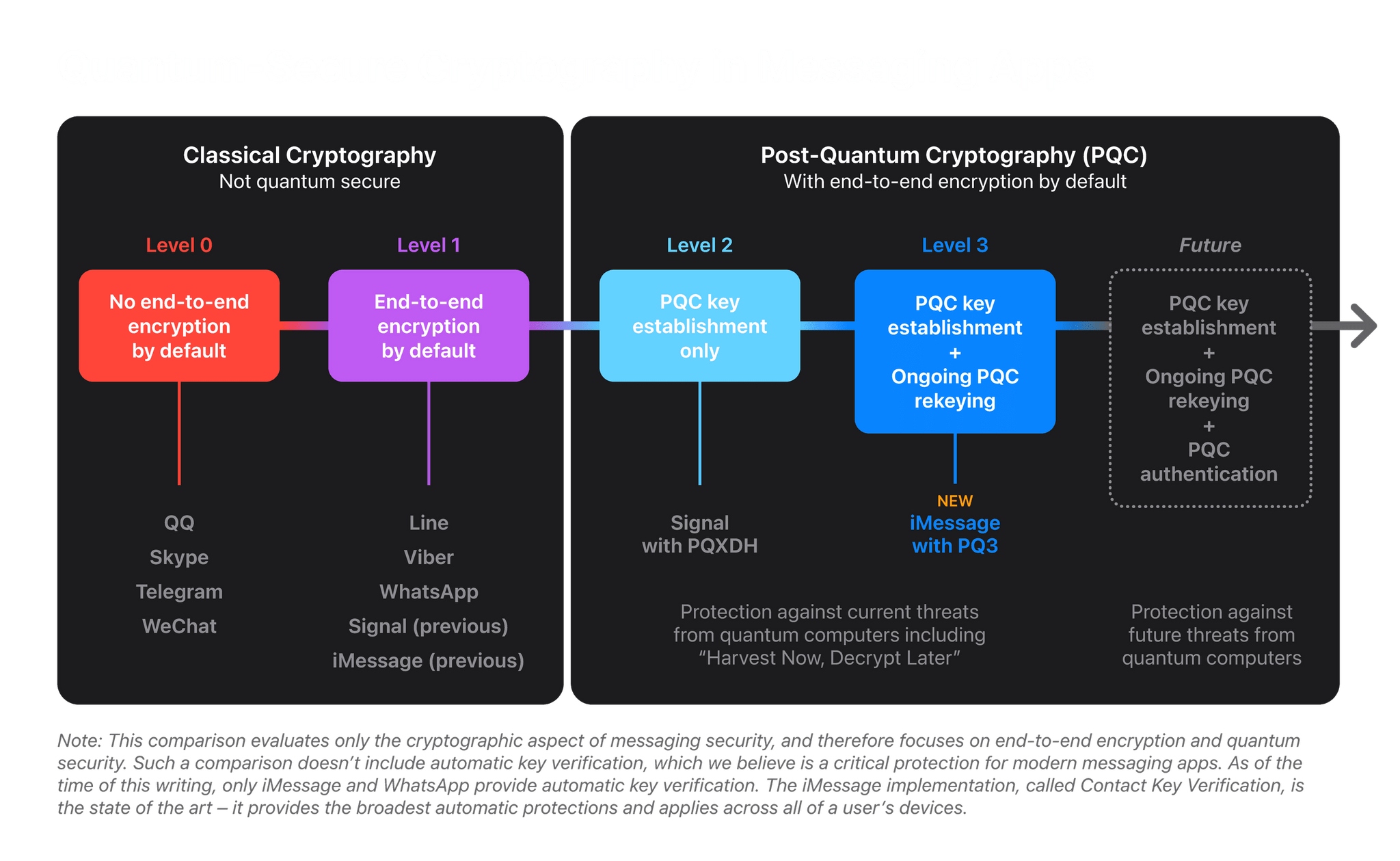
Yesterday, Apple’s Security Research website published a report on a cryptographic security upgrade coming to iMessage with the release of iOS 17.4, iPadOS 17.4, macOS 14.4, and watchOS 10.4 called PQ3. It’s a forward-looking, preemptive upgrade that anticipates a future where quantum computers will be able to defeat today’s cryptographic security with ease. That day isn’t here yet, but PQ3 is rolling out with the next series of Apple’s OS updates to protect against a scenario known as Harvest Now, Decrypt Later where bad actors collect vast amounts of encrypted data today, anticipating a future where it can be decrypted by quantum computers.
If you’ve heard the term quantum computing thrown around in the past and don’t know what it is, I highly recommend a couple of explainer articles by the MIT Technology Review that cover both quantum computers and post-quantum cryptography. But if the details don’t interest you, the bottom line is that PQ3 is being added to iMessage today in anticipation of a day in the future where today’s end-to-end encryption techniques don’t work anymore. Here’s how Apple’s paper explains it:
Historically, messaging platforms have used classical public key cryptography, such as RSA, Elliptic Curve signatures, and Diffie-Hellman key exchange, to establish secure end-to-end encrypted connections between devices. All these algorithms are based on difficult mathematical problems that have long been considered too computationally intensive for computers to solve, even when accounting for Moore’s law. However, the rise of quantum computing threatens to change the equation. A sufficiently powerful quantum computer could solve these classical mathematical problems in fundamentally different ways, and therefore — in theory — do so fast enough to threaten the security of end-to-end encrypted communications.
Although quantum computers with this capability don’t exist yet, extremely well-resourced attackers can already prepare for their possible arrival by taking advantage of the steep decrease in modern data storage costs. The premise is simple: such attackers can collect large amounts of today’s encrypted data and file it all away for future reference. Even though they can’t decrypt any of this data today, they can retain it until they acquire a quantum computer that can decrypt it in the future, an attack scenario known as Harvest Now, Decrypt Later.
PQ3 protects against a post-quantum world by setting up an iMessage conversation with a new post-quantum public key system and then periodically updating the keys so that if the keys are compromised, it won’t compromise the entire conversation. The system also uses existing cryptographic algorithms for portions of the encryption process that aren’t vulnerable to a Harvest Now, Decrypt Later scenario.
There is a lot of additional detail in Apple’s report, as you can imagine, including information about the review process that the new system has undergone and the way it is applied to iMessage in particular, which explains the design considerations that were necessary to apply these cryptographic techniques at the scale of iMessage in a way that doesn’t compromise users’ experience.
There’s more to be done to ramp up iMessage’s security even further as we approach a world where quantum computers are a threat to traditional cryptography. However, as Apple’s report concludes, with the imminent OS updates, iMessage will be “the global state of the art for protecting messages against Harvest Now, Decrypt Later attacks and future quantum computers.”
I’ve heard iMessage security get thrown under the bus a lot lately as an excuse Apple uses to protect its market dominance. There’s no reason that protecting customer communications and market-share can’t both be true. However, I think you’d be hard-pressed to read a report like this one and not come away believing that customer privacy and security are also a sincere goals at Apple.