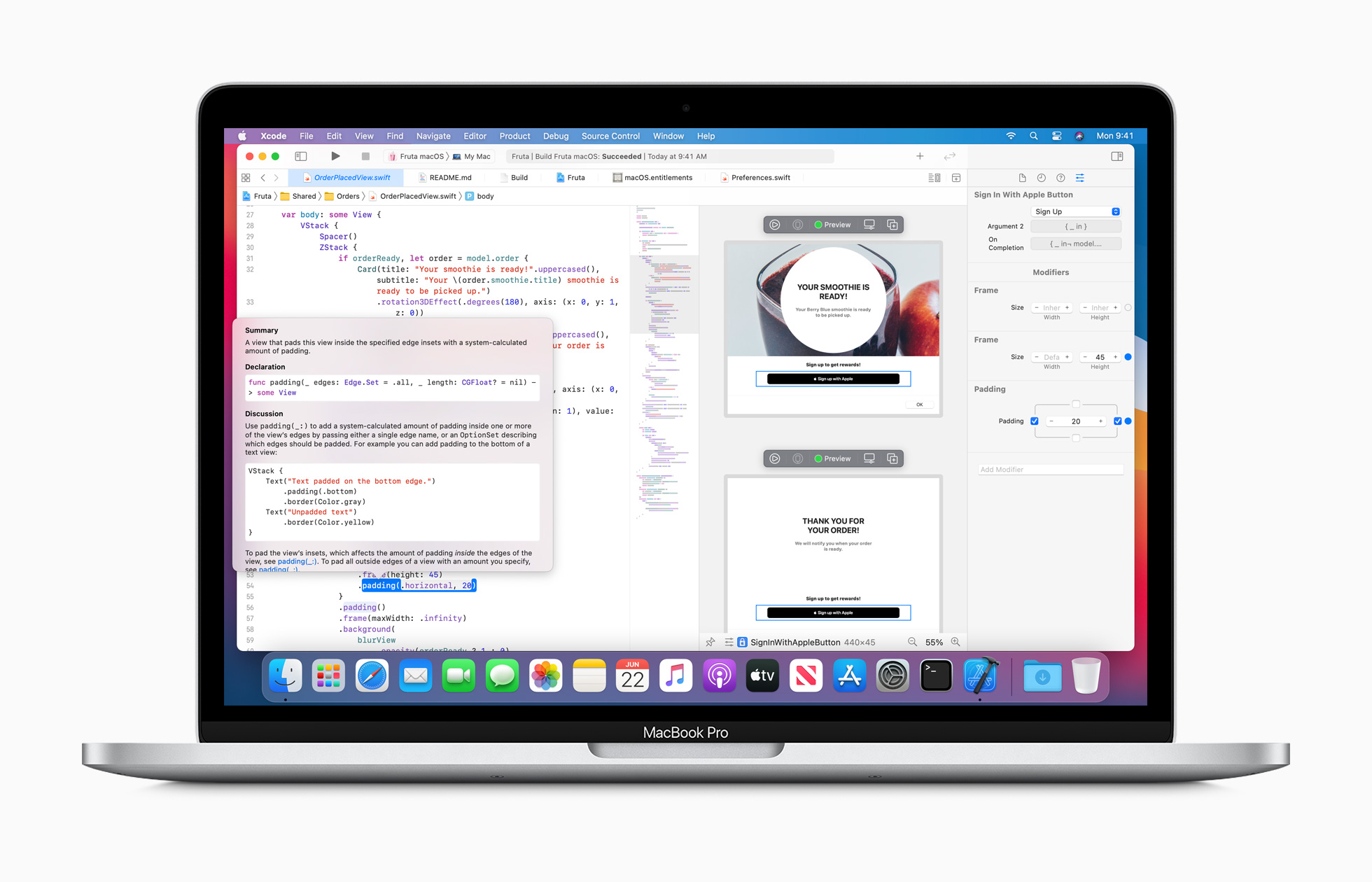
Echoes of the past were woven throughout Apple’s announcement that it is transitioning the Mac from Intel-based chips to its own architecture. During the keynote yesterday, Senior Vice President of Hardware Technologies Johny Srouji kicked things off by explaining the balance between performance and power consumption, something that drove the transition to Intel chips nearly 15 years go. Then, Craig Federighi introduced Universal 2 and Rosetta 2, software solutions that originated with the transition to Intel Macs.
It would be a mistake to conclude that the transition to Apple Silicon will be just like the last switch, though. The computing world is very different from 2006, and so is Apple’s lineup of products. The transition carries the promise of powerful, low-power Macs, but it also foreshadows a fundamental change in the relationship among Apple’s platforms that began with the introduction of Mac Catalyst, SwiftUI, and related initiatives. Where precisely these changes lead is not entirely clear yet, but one thing is for certain: the Mac is changing dramatically.
Yesterday, I covered macOS 11.0, known as Big Sur, which is as much a part of this transition as the Mac’s new system-on-a-chip (SoC) will be. Today, however, it’s worth taking a closer look at the hardware that was announced. It won’t be available to consumers until later this year, and the transition is expected to take two years. However, within a week or so, developers will begin receiving test kits that will allow them to start working on supporting the new hardware when the new Macs start shipping.